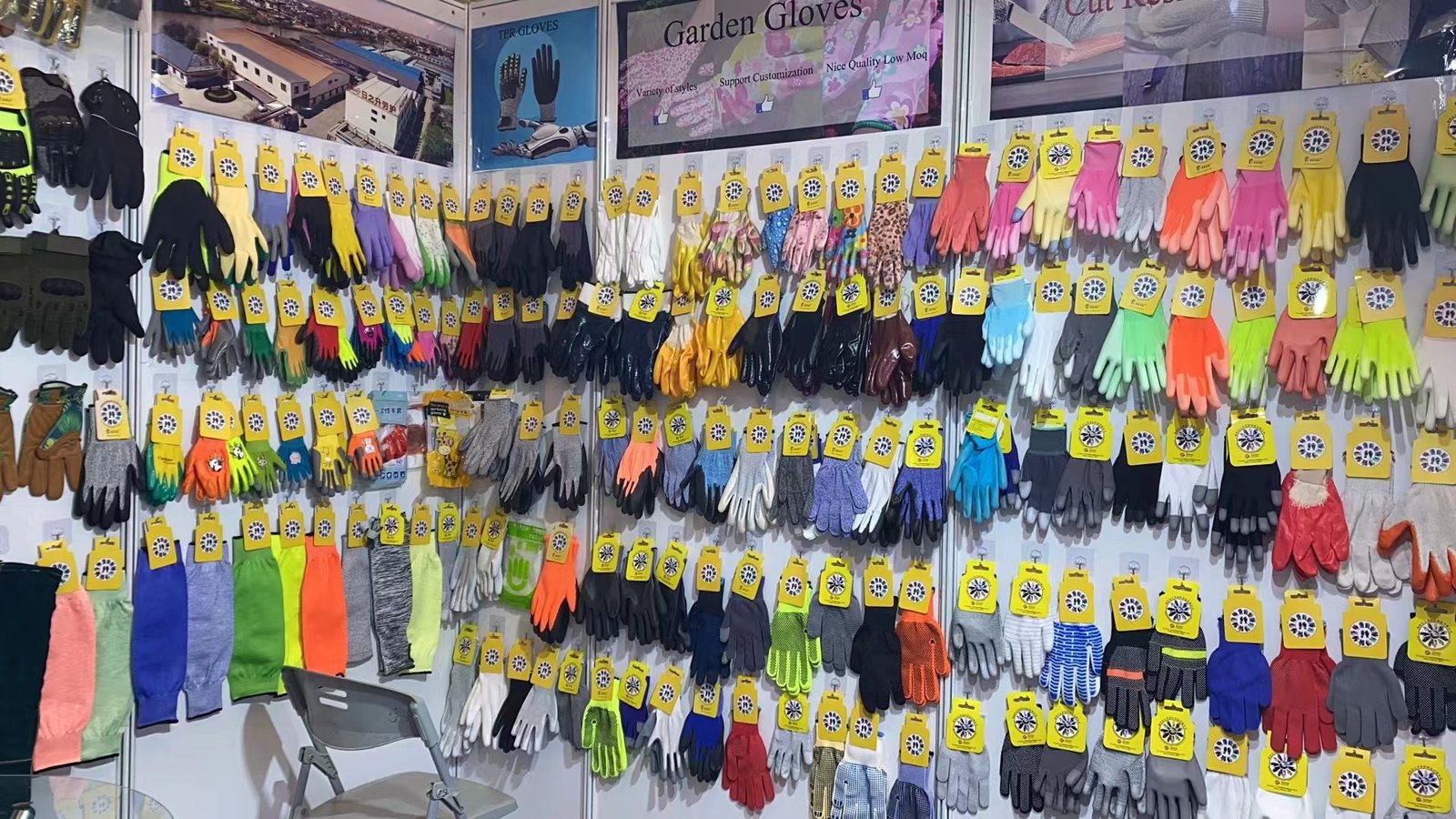
Why Work Gloves Matter (Safety + Productivity)
Work gloves do more than prevent injuries—they improve grip, reduce fatigue, and help workers stay productive in harsh environments. In industrial supply catalogs, common reasons to use work gloves include enhanced safety, improved grip and control (especially with nitrile/latex/PU coatings), and compliance with PPE standards.
Common hazards work gloves help reduce:
•Cuts/lacerations from sharp edges
•Abrasions from rough surfaces
•Punctures from wire, splinters, metal burrs
•Chemical exposure and chemical burns
•Heat and flame hazards
•Cold exposure and wet conditions
•Electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage in electronics
⸻
Work Gloves Types (By Hazard and Task)
Below are the most common types of work gloves and what they’re for. This mirrors what buyers expect from top-ranking pages, but with more depth than typical category pages.
1) General Handling Gloves (Daily work, warehouse, packaging)
Best for: light industrial tasks, warehouse picking, assembly, logistics
What to look for: breathable liner (nylon/polyester), palm coating (PU/nitrile/latex) for grip
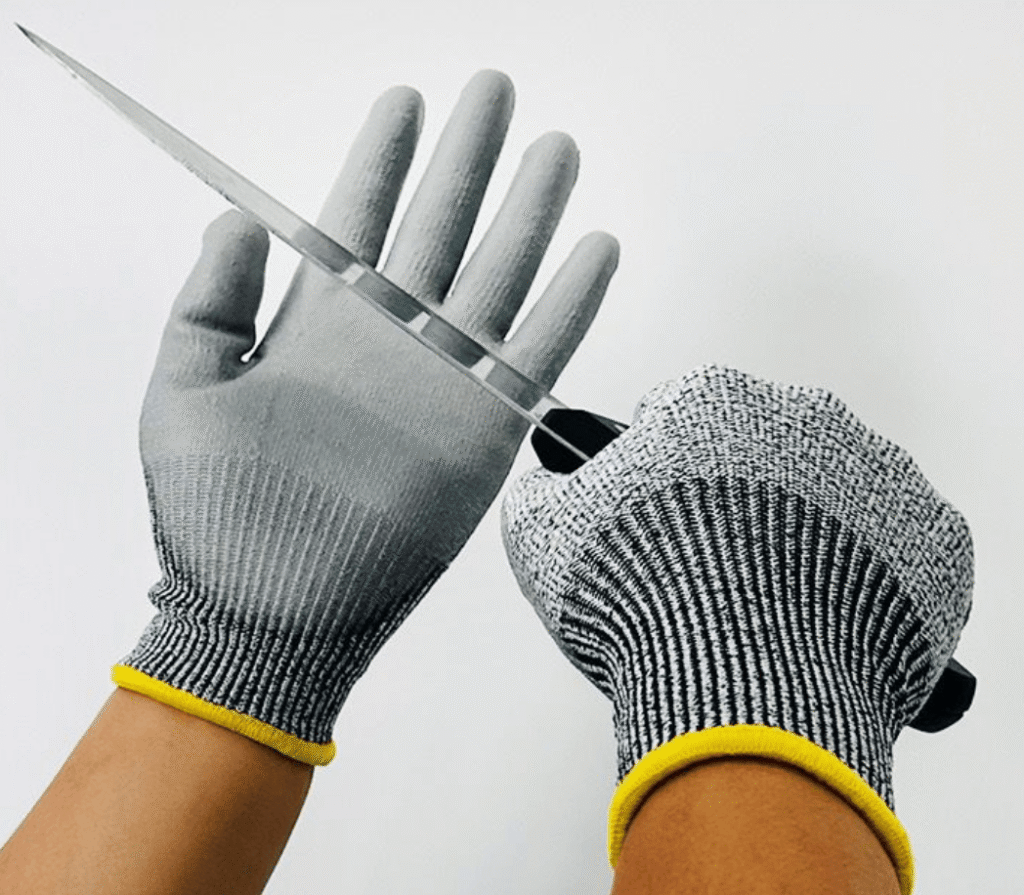
2) Cut-Resistant Gloves (Glass, metal, blades)
Best for: metal fabrication, glass handling, construction, utilities
What to look for: HPPE/UHMWPE/aramid blends, reinforced palms, certified cut levels
EN 388 is the major European standard for mechanical risks—abrasion, cut, tear, puncture, and optional impact.
3) Heat Resistant Gloves (Welding, ovens, foundry)
Best for: welding, hot parts handling, industrial ovens, automotive repair
Thermal protection gloves are commonly evaluated under EN 407 for heat/fire related tests (e.g., contact heat, convective/radiant heat, limited flame spread, molten metal splashes).
4) Chemical & Oil Resistant Gloves (Labs, maintenance, cleaning)
Best for: chemical handling, janitorial, automotive fluids, lab operations
EN ISO 374 is commonly used for chemical/micro-organism risks and classifies gloves as Type A/B/C based on permeation performance (breakthrough times and number of chemicals).
5) Cold / Waterproof / Insulated Gloves (Outdoor + cold storage)
Best for: cold warehouses, outdoor winter work, refrigerated logistics
EN 511 addresses protection against cold (convective/contact) and includes water resistance information.
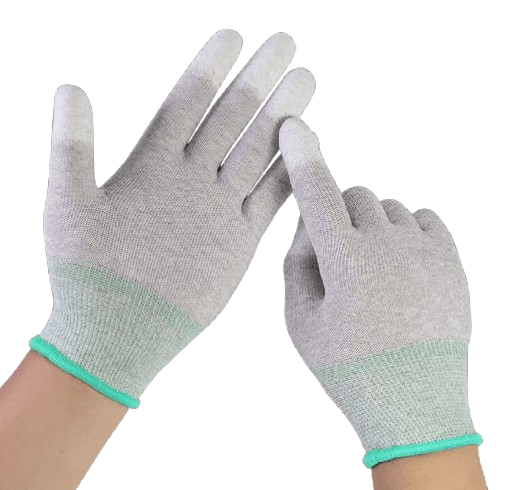
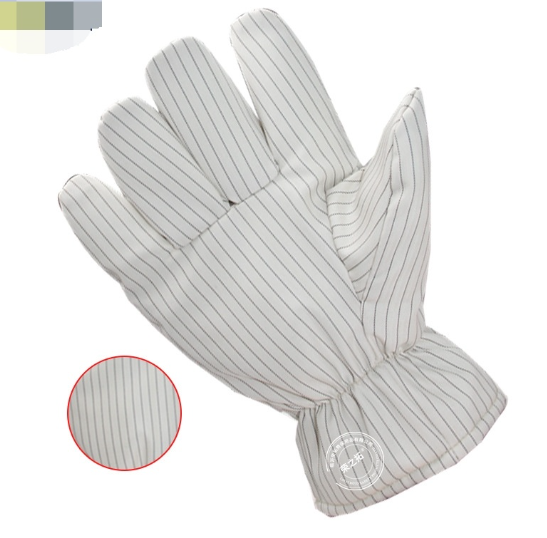
6) ESD / Anti-Static Gloves (Electronics, cleanroom)
Best for: electronics assembly, semiconductor, PCB handling
ESD-safe gloves reduce static discharge risk in sensitive environments. Industrial catalogs commonly list ESD gloves as a key application category for electronics work.
For tasks involving sharp edges, metal sheets, or glass,
cut resistant gloves provide enhanced hand protection while maintaining productivity. In environments requiring electrostatic discharge control,
ESD gloves are essential for protecting sensitive electronics. Disposable
nitrile gloves are commonly used for contamination control and light-duty protection.
⸻
Materials Explained (What Your Gloves Are Made Of)
Material / Coating Strengths Typical Uses Watch-outs
PU coating Great dexterity + clean grip electronics, light assembly, small parts less ideal for heavy oil
Nitrile coating Strong grip in oil/wet, durable automotive, warehouse, general handling thicker nitrile = less dexterity
Latex coating flexible, excellent dry grip construction, general handling latex allergy risk
Leather abrasion resistance, rugged construction, mechanical work less fine fingertip control
HPPE/UHMWPE/Aramid high cut resistance glass/metal handling match cut rating to hazard
Nitrile disposable chemical/oil barrier, latex-free labs, cleaning, food handling choose thickness for durability
Vinyl disposable economical for low-risk tasks low-hazard, short wear weaker chemical durability vs nitrile
Nylon liner breathable, comfortable daily general handling needs coating for grip
⸻
Standards & Ratings (How to Read Glove Markings)
If you want your page to outrank short catalog pages, you must explain ratings clearly. Here’s a buyer-friendly, SEO-friendly version.
EN 388 (Mechanical Risks)
EN 388 evaluates gloves against abrasion, blade cut, tear, puncture, and (where applicable) impact. The updated EN 388:2016+A1:2018 framework also references an ISO cut test method for certain gloves.
Plain-English tip:
•Higher numbers/letters = higher protection in that test area.
•Don’t buy “highest cut” automatically—higher cut gloves can be thicker and reduce dexterity.
ANSI/ISEA 105 (Cut Levels A1–A9)
In the U.S. market, ANSI/ISEA 105 uses an A1–A9 scale for cut resistance; higher levels mean greater cut protection.
Plain-English tip:
•A2–A4: light to medium sharp-edge work
•A5–A7: heavier industrial handling
•A8–A9: extreme cut risk scenarios
EN ISO 374 (Chemical / Micro-organism)
EN ISO 374 commonly marks chemical gloves as Type A/B/C depending on permeation performance and the number of chemicals meeting minimum breakthrough time criteria.
EN 407 (Heat / Fire)
EN 407 evaluates protection against thermal risks such as contact heat, convective/radiant heat, limited flame spread, molten metal splashes, etc.
EN 511 (Cold)
EN 511 covers protection against convective and contact cold and includes water penetration information.
⸻
How to Choose Work Gloves (A Practical 5-Step Method)
Step 1: Identify the hazard (not the glove)
•Sharp edges? → cut-resistant (EN 388 / ANSI cut)
•Chemicals? → chemical resistance (EN ISO 374)
•Heat/flame? → thermal protection (EN 407)
•Cold/wet? → insulated waterproof (EN 511)
•Electronics? → ESD-safe gloves
OSHA also emphasizes selecting appropriate hand protection when exposed to hazards such as harmful substances, cuts, abrasions, punctures, chemical/thermal burns, and temperature extremes.
Step 2: Match protection level to the task
Over-protection can reduce dexterity and cause accidents (dropping parts, poor tool control). Choose the right level, not always the highest.
Step 3: Choose material and coating
•Oily/wet handling: nitrile coating
•Clean handling & precision: PU coating
•Heavy abrasion: leather or reinforced palms
Step 4: Fit and comfort
Correct fit improves control, grip, and reduces fatigue—especially for long shifts.
Step 5: Consider environment + duration
•Hot climate: breathable liners
•Cold storage: insulation + water resistance
•Cleanroom: low-lint materials + ESD controls
⸻
Industry Applications (Use-Case Matching)
Catalog pages often list industries; we’ll expand it into “what to choose and why”, like strong ranking pages do.
•Construction: abrasion + cut risk → heavy-duty / cut-resistant
•Automotive: oil + tool grip → nitrile-coated + impact/cut options
•Manufacturing: abrasion + repetitive handling → coated general handling
•Oil & Gas: chemical/oil exposure → chemical resistant + grip
•Electronics: ESD control → ESD gloves
These application buckets are consistent with how industrial suppliers explain work glove usage across industries.
⸻
Recommended Work Gloves by Scenario (Fast Buyer Table)
Scenario Recommended Glove Type Key Feature
Handling boxes in warehouse PU or nitrile coated work gloves grip + comfort
Metal sheet handling Cut-resistant gloves EN 388 / ANSI cut level
Welding & hot parts Heat resistant gloves EN 407 thermal tests
Chemical cleaning / solvents Nitrile gloves chemical resistance (EN ISO 374 when applicable)
Cold storage picking Insulated warm gloves EN 511 cold protection
PCB assembly ESD / anti-static gloves static dissipation
⸻
Care, Inspection & Replacement (Most sites forget this)
Daily checks
•Holes, tears, worn fingertips/palms
•Contamination (oil, chemicals)
•Loss of grip coating
Replace gloves when
•Grip coating is smooth and slippery
•Liner is torn / seams split
•Chemical exposure occurred beyond glove rating
⸻
FAQ
Q1: What are work gloves used for?
Work gloves protect hands from cuts, abrasions, punctures, chemical exposure, heat, and harmful temperature extremes.
Q2: What’s the difference between EN 388 and ANSI cut ratings?
EN 388 is a European mechanical risk standard (abrasion/cut/tear/puncture/impact), while ANSI/ISEA 105 uses A1–A9 cut levels commonly used in the U.S.
Q3: Which gloves are best for oily or wet handling?
Nitrile-coated work gloves are widely chosen for strong grip and durability in oily/wet conditions (common industrial selection logic).
Q4: Do I need special gloves for electronics?
Yes—ESD/anti-static gloves are recommended for electronics work to reduce static discharge risk.
Q5: What standard applies to chemical resistant gloves?
EN ISO 374 is commonly used for chemical/micro-organism risks and includes Type A/B/C classifications based on permeation performance.
Electrostatic discharge poses severe risks in electronics manufacturing, semiconductor production, and precision engineering. HORBEST ESD gloves are engineered to dissipate static electricity, preventing damage to sensitive components and ensuring operator safety.
Slash, puncture, and cut injuries are common in construction, metalworking, food processing, and packaging. HORBEST Cut Resistant Gloves are certified to global cut protection standards, providing reliable defense against sharp tools and materials.
High-temperature environments such as welding, foundries, kitchen operations, and automotive repair require gloves that withstand extreme heat without sacrificing protection. HORBEST Heat Resistant Gloves are built to shield hands from burns and thermal stress.
Nitrile gloves are a versatile choice for chemical handling, medical settings, and food service—offering superior chemical resistance and latex-free comfort. HORBEST Nitrile Gloves are a top choice for professionals seeking durability and hygiene.
Latex gloves are prized for their exceptional elasticity and tactile sensitivity, making them ideal for tasks requiring precision. HORBEST Latex Gloves combine natural comfort with reliable protection.
Nylon gloves are lightweight, breathable, and cost-effective—perfect for general-purpose tasks where comfort and flexibility are key. HORBEST Nylon Gloves are a staple in warehouses, manufacturing, and light assembly.
PU (Polyurethane) coated gloves bridge the gap between dexterity and grip, making them a favorite for tasks involving small parts or slippery surfaces. HORBEST PU Coated Gloves deliver consistent performance in diverse workplaces.
At HORBEST, we don’t just manufacture gloves—we engineer solutions that prioritize safety, comfort, and durability. Here’s what sets us apart:
Whether you’re safeguarding workers in a semiconductor cleanroom, a construction site, or a commercial kitchen, HORBEST has the perfect work glove for the job. Don’t compromise on safety—choose gloves that are trusted by professionals worldwide.
Keywords: HORBEST work gloves, ESD gloves, cut resistant gloves, heat resistant gloves, nitrile gloves, latex gloves, nylon gloves, PU coated gloves, industrial safety gloves, premium PPE gloves